🚀 Emerging Technologies Redefining Medicine: From AI Screenings for Diabetic Retinopathy 👁️ and 3D-Printed Cardiac Valve Models 🫀 to VR Education for Patients 💻
Supplement to The 'Med AI' Capsule Newsletter 🤖🩺🚀
Dear Med AI Enthusiast,
Welcome to this fortnightly special feature, a curated blend of academic and industrial insights, complementing The 'Med AI' Capsule, your fortnightly news digest. 📰
Dive into the transformative world of artificial intelligence and emerging technologies shaping the future of medicine. ⚕️
Stay ahead with insights from our exploration of how these advancements are redefining healthcare. 🚀
In today’s supplement:
3 Med AI Research Updates
2 Emerging Tech Research Updates
1 Infographic
Industry Showcase
Reading Time: 5-7 minutes
Med AI Research Updates 🔬
1. 👁️ AI Assists in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Real-World Settings Using Smartphones

Key Findings: An AI system deployed in the diabetic retinopathy screening program in Dominica demonstrated 77.5% sensitivity and 91.5% specificity in detecting referable cases when compared to a specialist grader.
Conclusion: The reasonable accuracy achieved highlights AI's potential to assist diabetic retinopathy screening programs in middle-income countries, helping address resource constraints.
Limitations: The study revealed lower AI performance versus prior validations, constrained by image quality limitations, model gaps in identifying diverse retinal pathologies, risks of bias from inadequate patient recall infrastructure, and potential gender inequities in screening participation.
2. 🎥 AI-Assists in Better Detection of Vocal Cords in Difficult Video Laryngoscopy
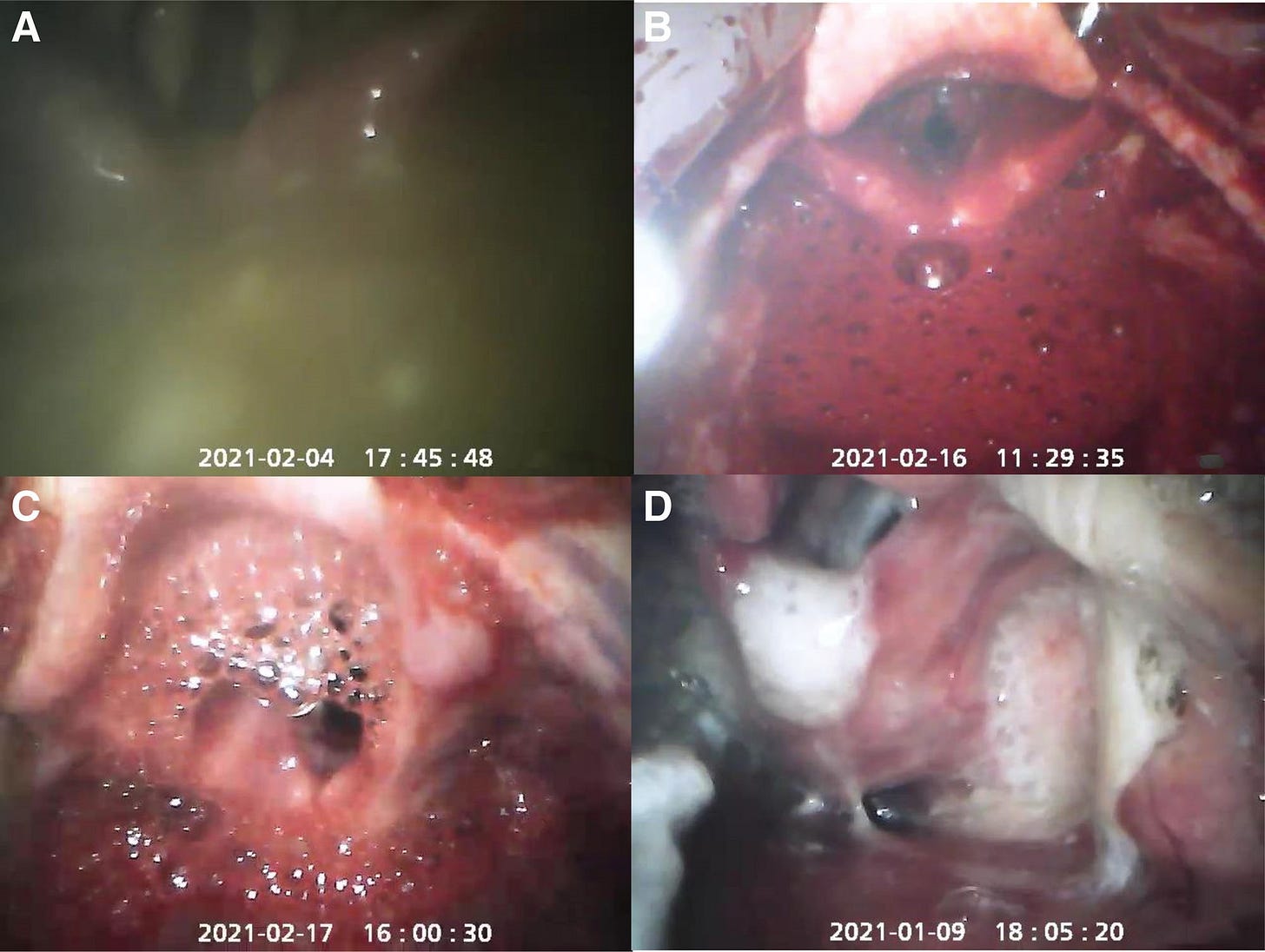
Key Findings: A new AI algorithm based on the YOLOv4 model demonstrated high accuracy (F1 score 0.808-0.906) in detecting vocal cords from video laryngoscopy images to assist emergency intubation.
Conclusion: The algorithm shows potential for integration in airway management procedures to improve clinician efficiency and patient safety.
Limitations: Performance differences across laryngoscope devices needs evaluation. Clinical skill improvement was not assessed. Bounding box labeling and other AI models need further analysis.
3. 🤖 Machine Learning (ML) Models Cut Pediatric Hospital Waiting Times

Key Findings: Machine learning models predicted outpatient waiting times in a Chinese pediatric hospital with higher accuracy vs linear regression, improving efficiency.
Conclusion: The Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT) model demonstrated particular effectiveness, highlighting ML's potential in optimizing hospital workflows.
Limitations: Single-center design limits validation. Departmental combinations reduced precision. Pre-pandemic data was excluded.
Emerging Tech Research Updates 🔬
1. 🖨️ Three-dimensional Printing of Mitral Valve Models Enhances Cardiology Fellow Training
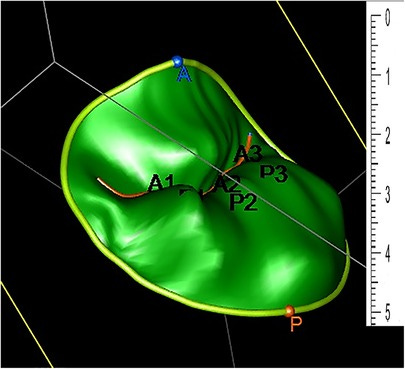
Key Findings: High-fidelity three-dimensional Mitral Valve Models (3D MVM) printed from echocardiography significantly improved the understanding of normal anatomy and pathology among cardiology fellow physicians in training.
Conclusion: The study indicates the positive impact of printed 3D MVMs on cardiology trainees' comprehension of mitral valve anatomy and pathology, surpassing the insights gained from 3D echocardiography images alone.
Limitations: The study's limited participant size highlights the potential of 3D printed models, but broader investigations involving more participants and diverse printing materials are recommended to thoroughly evaluate their effectiveness in medical education.
2. 🌐 Virtual Reality Enhances Patient Education on Hypertension

Key Findings: Virtual Reality (VR) demonstrates superior effectiveness in enhancing hypertension knowledge compared to traditional education (VR: median 14, IQR 3; traditional: median 10, IQR 5, p < 0.001), with high participant satisfaction noted in both groups and particularly notable benefits observed among older women.
Conclusion: VR outperforms traditional education. Tailoring to groups such as older women can optimise learning.
Limitations: Key limitations include a single-center design limiting generalizability, unassessed factors like patients' educational background and willingness to acquire knowledge, and considerations for accessibility barriers before widespread implementation, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Infographic 📊
Industry Showcase 👨🏭
Lunit Global - a public company, leads the charge in conquering cancer through its medical AI software—Lunit INSIGHT for early-stage cancer detection and Lunit SCOPE for optimizing cancer treatment. The company collaborates globally with industry leaders like Fujifilm, GE Healthcare, Philips, Guardant Health, and others to provide these AI solutions to medical institutions worldwide.
Enlitic - dedicated to transforming healthcare through artificial intelligence, intelligently managing data to enhance clinical workflows, standardize DICOM studies, and create a real-world evidence medical image database. Their solutions, such as ENDEX and ENCOG, streamline data processing, remove PHI intelligently, and address long-standing challenges in radiology, resulting in improved efficiency, reduced workload for administrators, and opportunities for additional revenue streams in healthcare.
IrisVision - an innovative wireless virtual reality headset leveraging advanced VR technology, utilizing a smartphone camera for image transmission. NIH-approved and designed for people with low vision, it can be worn over distance glasses, providing a revolutionary solution for the visually impaired, enabling greater independence for legally blind individuals.
Stay tuned for our upcoming editions as we explore the latest breakthroughs and dive deep into the transformative power of artificial intelligence and emerging technologies, shaping a healthier future. 🚀
Warm regards,

P.S.: If you're a medical professional intrigued by artificial intelligence, but not sure where to start, feel free to reach out to me for personalised guidance.
You can also check out and join our educational WhatsApp Community for Medical Professionals.




