🤖 Revolutionizing Patient Care with AI: From Twitter Insights on Painkillers to Predictive Models in Cancer Treatment and Early Warning Systems 🚀
Supplement to The 'Med AI' Capsule Newsletter 🤖🩺🚀
Dear Med AI Enthusiast,
Welcome to this fortnightly special feature, a curated blend of academic and industrial insights, complementing The 'Med AI' Capsule, your fortnightly news digest. 📰
Dive into the transformative world of artificial intelligence and emerging technologies shaping the future of medicine. ⚕️
Stay ahead with insights from our exploration of how these advancements are redefining healthcare. 🚀
In today’s supplement:
3 Med AI Research Updates
2 Emerging Tech Research Updates
1 Infographic
Industry Showcase
Reading Time: 5-7 minutes
Med AI Research Updates 🔬
1. 📰 Analyzing Painkillers on Twitter: AI Reveals Public Opinion and Trends ⚕️

Key Findings: Twitter discussions about paracetamol, tramadol, and codeine are frequent, with patients being the most active participants. Healthcare professionals and institutions get more likes and retweets, highlighting their influence in these conversations.
Conclusion: The study reveals distinct differences in how Twitter users discuss these painkillers, emphasizing the need for monitoring social media for insights into drug use trends and public perception.
Limitations: The research faces challenges in capturing the full spectrum of relevant tweets due to diverse language use and may not fully represent the general population's views, with potential shifts in perspectives over time.
2. 📊 Machine Learning in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Enhancing Survival Predictions and Treatment Guidance ⚕️
Key Findings: The study developed machine learning models that outperform standard methods in predicting survival for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. These models also provide personalized treatment recommendations, showing improved survival rates for patients following these suggestions.
Conclusion: This novel approach using machine learning offers a significant improvement in prognostic evaluations and treatment strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma, potentially revolutionizing patient care in this field.
Limitations: Model accuracy is constrained by the SEER database's data quality and requires broader validation and data integration for wider clinical use.
3. 🚨 Deep Learning for Early Warning in Cancer Care: A New Frontier in Patient Monitoring 🏥
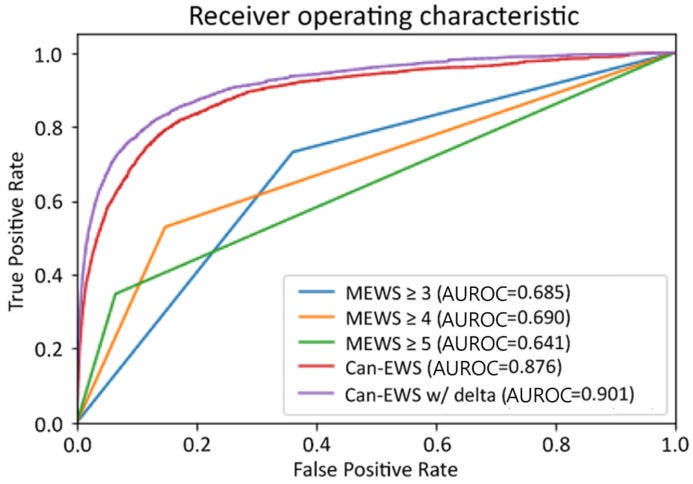
Key Findings: The study developed a deep learning-based early warning score (Can-EWS) for cancer patients, significantly outperforming traditional methods in predicting clinical deterioration. Can-EWS V2 demonstrated superior accuracy in detecting in-hospital cardiac arrests and ICU transfers.
Conclusion: Can-EWS represents a significant advancement in monitoring and predicting clinical deterioration in cancer patients, offering a more precise and efficient tool for hospital settings.
Limitations: The study's retrospective nature and single-institution data limit its generalizability, and the deep learning model's "black box" nature requires further exploration to understand its decision-making process.
Emerging Tech Research Updates 🔬
1. 🔩 3D-Printed Titanium Bone Plates: Charting New Horizons in Craniofacial Surgery 🦴
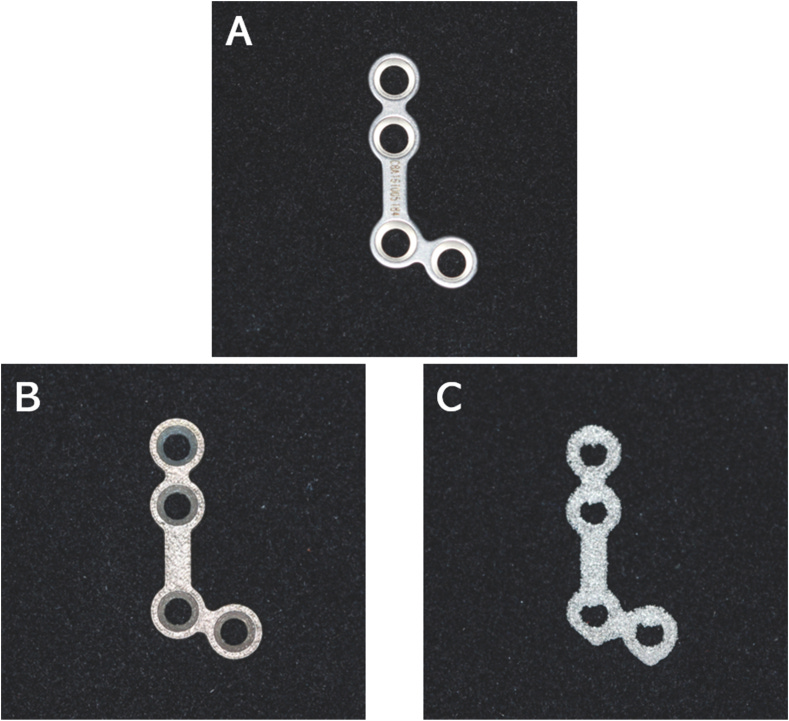
Key Findings: This study found that 3D-printed craniomaxillofacial bone plates have superior bending strength compared to standard machined plates. However, improvements are needed in fatigue resistance and reducing internal defects.
Conclusion: The 3D-printed titanium bone plates show promising mechanical performance and surface suitability for clinical use, but further refinement is required to enhance their fatigue resistance and internal structure.
Limitations: There's a need for more comprehensive studies to address the fatigue resistance and internal defects found in the 3D-printed plates before they can be widely adopted in clinical settings.
2. 🕶️ Exploring Virtual Reality for Post-Surgery Pain Relief: Study Reveals Patients' Insights 🩺

Key Findings: Patients benefited from self-administered VR for post-surgical pain management, favoring intuitive 3D VR devices with diverse apps and 2-3 daily sessions lasting 10-15 minutes, highlighting the importance of personalization.
Conclusion: Self-administered VR holds promise for post-surgical pain management, emphasizing the need for tailored interventions and awareness among patients and healthcare professionals.
Limitations: Focus on post-surgical patients, age-related technology experiences, potential participant bias, lack of clinician input, and limited practical organizational details.
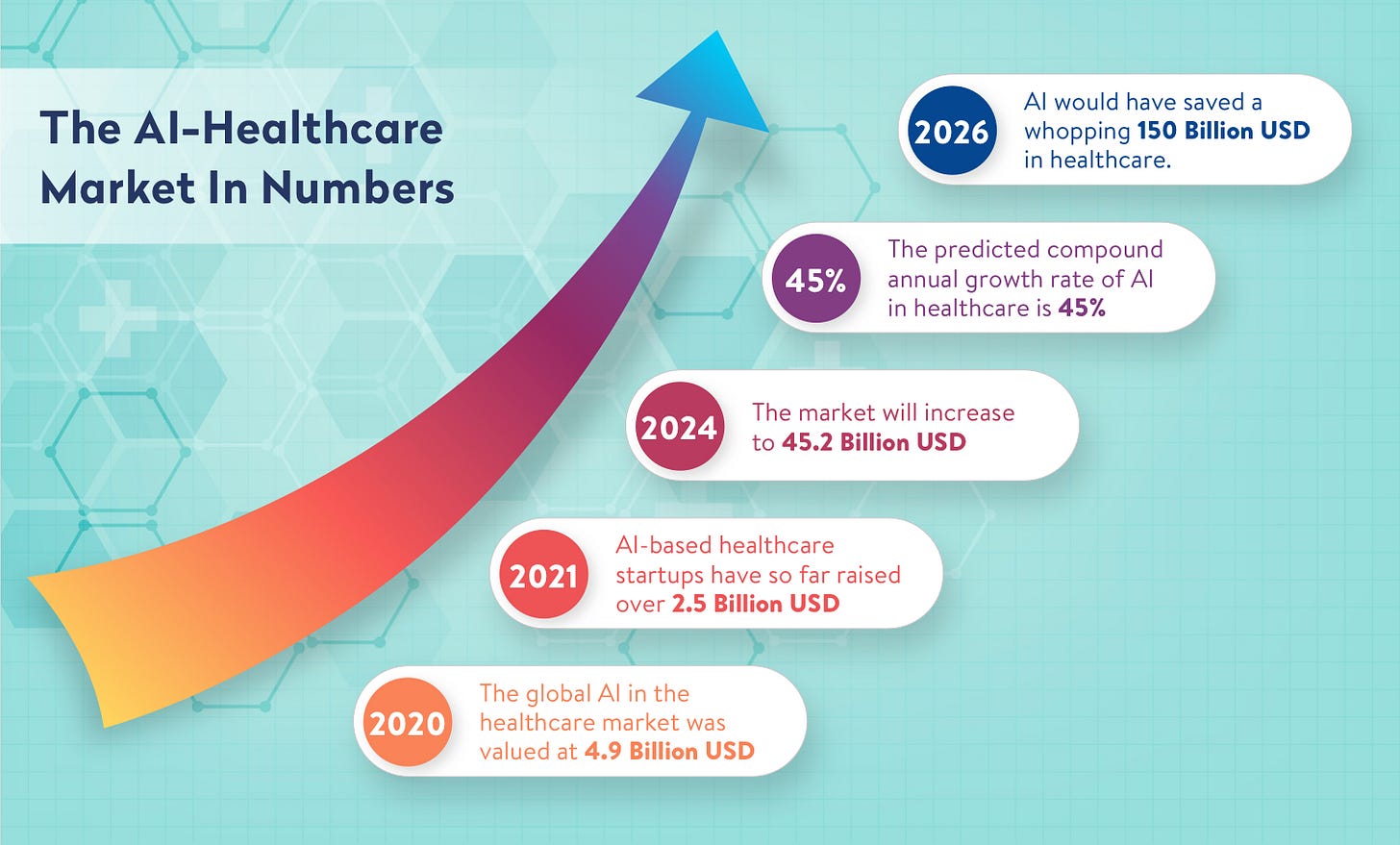
Infographic 📊
Industry Showcase 👨🏭
Aindra - a healthcare company utilizing AI for affordable healthcare solutions and disease detection. Their Astra platform, including CervAstra, aims to democratize healthcare access with a focus on cervical cancer detection.
Insilico Medicine - a leading biotech company that uses generative AI to accelerate drug discovery and development. The company has a proprietary platform called Pharma.AI that covers biology, chemistry and clinical development.
Twin Health - uses Whole Body Digital Twin™ technology to reverse type 2 diabetes through AI-based precision treatment, with a focus on personalized plans.
Stay tuned for our upcoming editions as we explore the latest breakthroughs and dive deep into the transformative power of artificial intelligence and emerging technologies, shaping a healthier future. 🚀
Warm regards,

P.S.: If you're a medical professional intrigued by artificial intelligence, but not sure where to start, feel free to reach out to me for personalised guidance.
You can also check out and join our vibrant Med AI WhatsApp Community for Medical Professionals.